Table of Contents
What is Chest Pain?
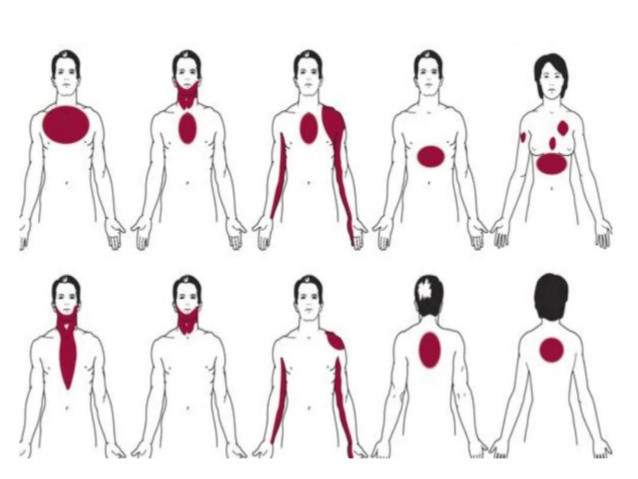
Chest pain is a common complaint that can vary in intensity and duration. It can range from a sharp stab to a dull ache. Sometimes, it feels crushing or burning. In certain cases, the pain travels up the neck, into the jaw, and then radiates to the back or down one or both arms.

Types:
Cardiac Chest Pain
1. Angina: A type of pain caused by reduced blood flow to the heart. It often occurs during physical exertion and is relieved by rest.
2. Heart Attack: This occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked. It is a medical emergency.
Non-Cardiac Chest Pain
1. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): This type of pain is caused by stomach acid flowing back into the esophagus.
2. Musculoskeletal Pain: This can result from inflammation or injury to the chest wall muscles and bones.
Causes of Chest pain:
The pain can be caused by various underlying reasons:
- Heart-related issues: Angina, heart attack, and pericarditis.
- Lung-related issues: Pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, and pleurisy.
- Gastrointestinal issues: GERD, esophageal spasms, and gallstones.
- Muscle and bone issues: Costochondritis and rib fractures.
- Mental health issues: Anxiety and panic attacks.
Symptoms:
The symptoms can vary depending on the cause. Common symptoms include:
- Sharp or dull pain: The pain can be intense or mild.
- Radiating pain: The pain may spread to the arms, back, neck, or jaw.
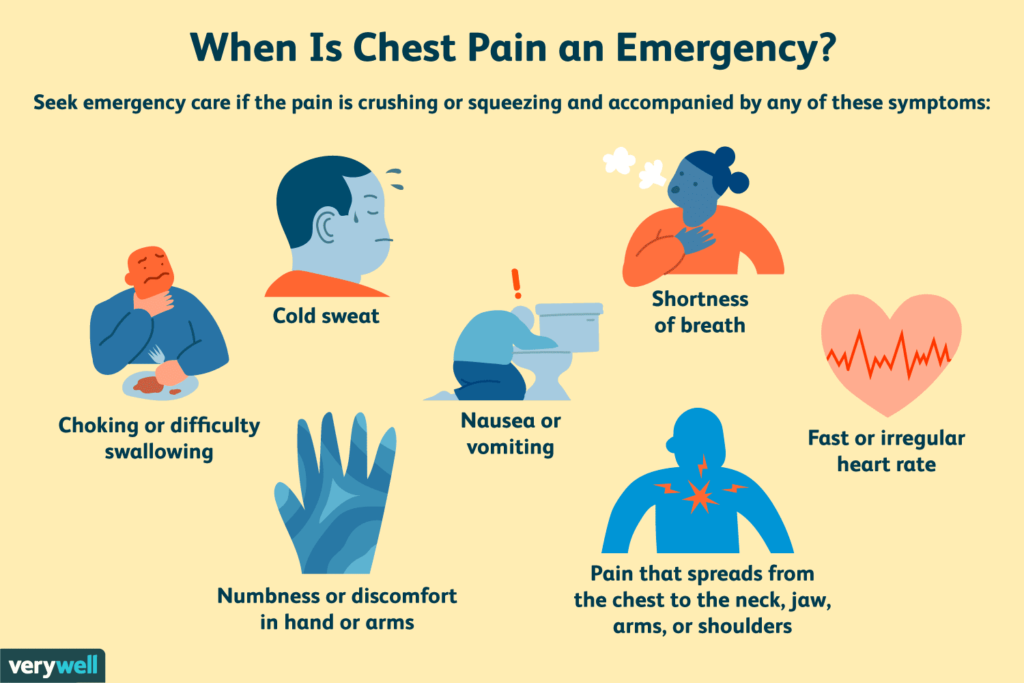
- Shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing can accompany too.
- Sweating: Cold sweats can occur, especially with cardiac issues.
- Nausea: Feeling sick to the stomach is common with heart-related angina.
Treatment:
The treatment depends on the underlying cause:
- Medications: Nitroglycerin, aspirin, and clot-busting drugs for heart-related pain.
- Lifestyle changes: Diet, exercise, and quitting smoking to improve heart health.
- Medical procedures: Angioplasty, stent placement, or surgery for severe cases.
- Therapies: Physical therapy and pain management for musculoskeletal issues.
- Mental health support: Counseling and medication for anxiety-related chest pain.
- Treatments for other causes of angina include:
- lung reinflation for a collapsed lung, which your doctor will perform by inserting a chest tube or related device.
- antacids or certain procedures for acid reflux and heartburn, which are used to treat the symptoms.
Prevention:
Preventing chest pain involves adopting a healthy lifestyle and managing existing health conditions. Here are some preventive measures:
- Regular exercise: Helps maintain a healthy heart and body weight.
- Healthy diet: Reduces the risk of heart disease and other health issues.
- Quit smoking: Smoking cessation significantly lowers the risk of heart disease.
- Stress management: Techniques like meditation and yoga can reduce stress levels.
- Regular check-ups: Monitor and manage chronic conditions like hypertension and diabetes.
- Avoid or limit alcohol.
- Don’t smoke.
- Eat a healthy diet.
- Exercise regularly.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Manage other health conditions related to heart disease.
- Reduce stress.
- Get 7 to 9 hours of sleep a day.
How chest pain is diagnosed?
Seek emergency treatment immediately if you think you may be having a heart attack and especially if your chest pain is new, unexplained, or lasts more than a few moments.
Your doctor will ask you some questions, and your answers can help them diagnose the cause of your pain. Be prepared to discuss any related symptoms and to share information about any medications, treatments, or other medical conditions you may have.
Diagnostic tests:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). This quick test measures the electrical activity of the heart. …
- Blood tests. Certain heart proteins slowly leak into the blood after heart damage from a heart attack. …
- Chest X-ray. …
- Computerized tomography (CT) scan.
- Stress test.
- Coronary angiogram.