Table of Contents
Introduction to Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic health condition that affects millions worldwide. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatments is crucial for managing the disease effectively.
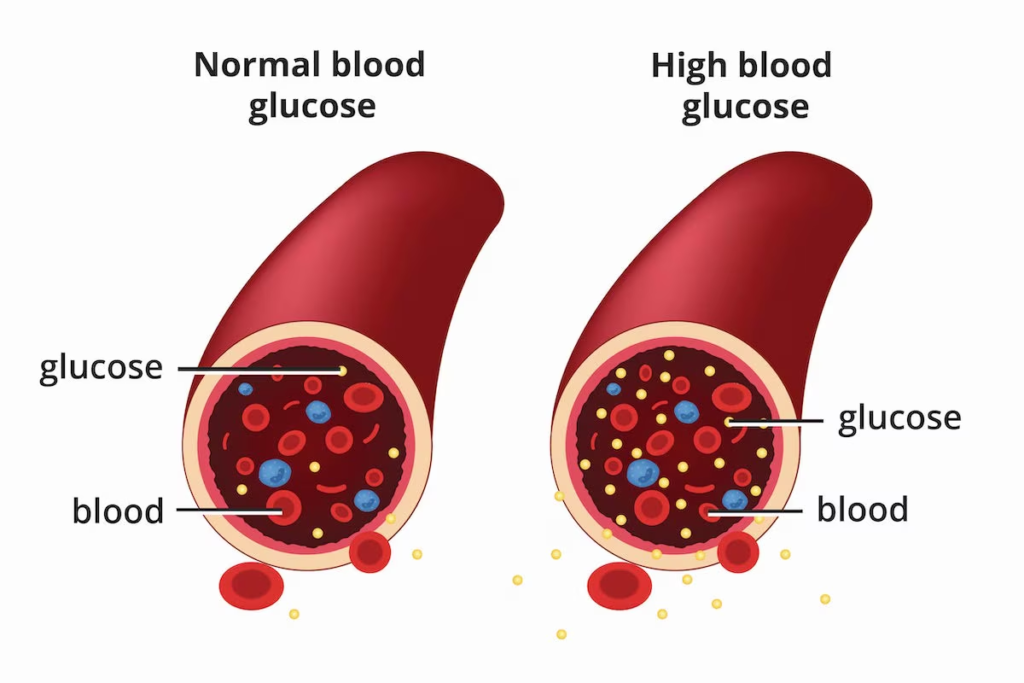
Normal Blood Sugar Levels
Maintaining normal blood sugar levels is essential for overall health. For most individuals, normal fasting blood sugar levels range from 70 to 99 mg/dL. Post-meal levels should be less than 140 mg/dL.
Initial Symptoms of Diabetes Mellitus
Early detection of diabetes can prevent severe complications. Common initial symptoms include:
- Increased thirst and frequent urination
- Extreme hunger
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
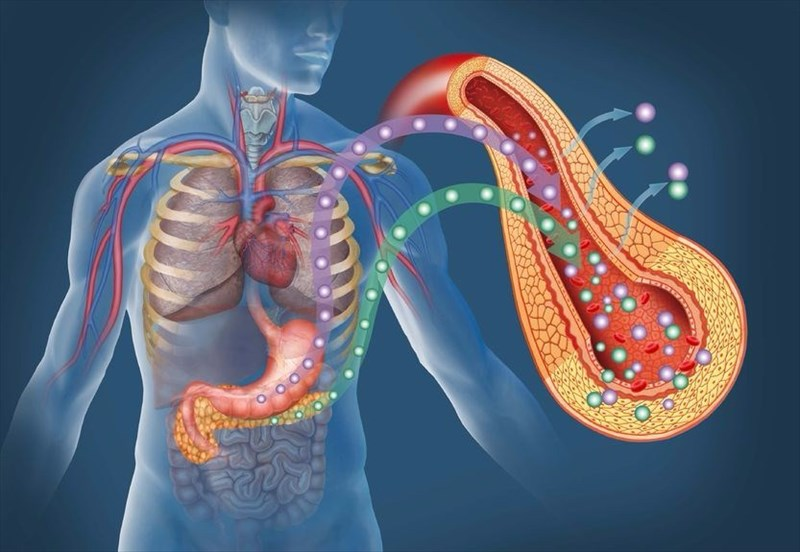
Causes of Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes can result from various factors. Key causes include:
- Genetic predisposition
- Autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing cells
- Lifestyle factors such as poor diet and physical inactivity.
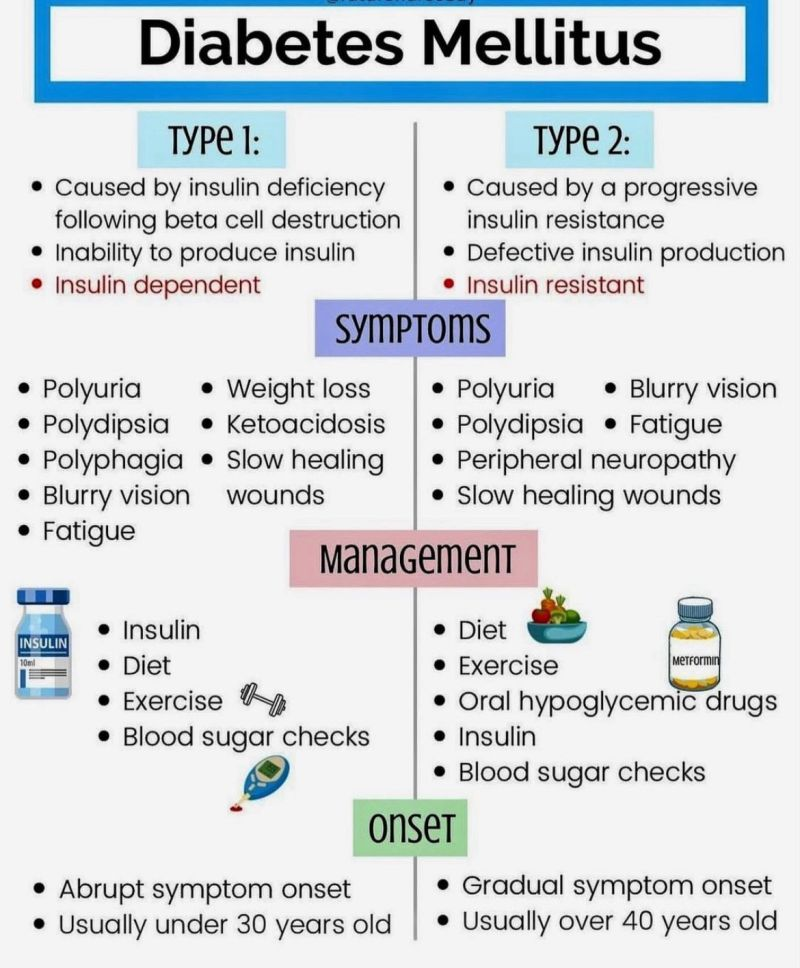
Types of Diabetes Mellitus
There are several types of diabetes, each with unique characteristics:
- Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition where the body attacks insulin-producing cells.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Often linked to lifestyle factors and insulin resistance.
- Gestational Diabetes: Occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after childbirth.
- Prediabetes: Blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not yet high enough to be classified as diabetes.
Onset of Diabetes Mellitus
The onset of diabetes varies with the type. Type 1 diabetes often appears in childhood or adolescence. Type 2 diabetes typically develops in adults over 45, but younger individuals are increasingly affected due to lifestyle changes. Gestational diabetes emerges during pregnancy.
Complications of Diabetes Mellitus
Without proper management, diabetes can lead to severe complications such as:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Nerve damage (neuropathy)
- Kidney damage (nephropathy)
- Eye damage (retinopathy)
- Foot problems due to poor circulation and nerve damage
Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus
Managing diabetes involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medical treatments:
- Diet: Emphasize a balanced diet rich in fiber, whole grains, and vegetables.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity helps control blood sugar levels.
- Medications: Insulin and oral medications are prescribed based on the type and severity of diabetes.
- Monitoring: Regular blood sugar monitoring is crucial for effective management.
Mortality Rate and Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes significantly impacts mortality rates. Complications such as heart disease and stroke are leading causes of death among diabetic patients. However, with proper management, individuals can lead long, healthy lives.
Introduction to Diabetes Management
Managing diabetes is crucial for preventing complications and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. This guide provides an in-depth look at effective strategies for diabetes management.
Healthy Eating for Diabetes Management
A balanced diet is the cornerstone of diabetes management. Key dietary tips include:
- Eat Balanced Meals: Incorporate a mix of vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Control Portion Sizes: Smaller portions help manage blood sugar levels.
- Limit Sugar and Refined Carbs: Avoid sugary drinks, sweets, and white bread.
- Increase Fiber Intake: Foods like fruits, vegetables, and legumes are beneficial.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
Regular Physical Activity
Exercise is essential for managing diabetes. Benefits of regular physical activity include:
- Improves Insulin Sensitivity: Helps your body use insulin more efficiently.
- Lowers Blood Sugar Levels: Exercise can reduce blood sugar for hours after activity.
- Aids Weight Management: Helps maintain a healthy weight, reducing the risk of complications.
- Enhances Cardiovascular Health: Strengthens the heart and improves circulation.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is vital. Tips for effective monitoring include:
- Set a Schedule: Check your blood sugar levels at the same times each day.
- Use a Reliable Glucometer: Ensure your device is accurate and properly calibrated.
- Keep a Log: Record your readings to track trends and identify patterns.
- Know Your Targets: Work with your healthcare provider to establish target ranges.
Medication Management
Medications play a significant role in diabetes management. Key points include:
- Follow Prescriptions: Take medications exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
- Understand Your Medications: Know how each medication works and its potential side effects.
- Store Medications Properly: Keep them in a cool, dry place and check expiration dates.
- Communicate with Your Doctor: Report any issues or side effects promptly.
Stress Management
Stress can impact blood sugar levels. Effective stress management techniques include:
- Practice Relaxation Techniques: Try deep breathing, meditation, or yoga.
- Stay Active: Physical activity can reduce stress levels.
- Get Adequate Sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Seek Support: Talk to friends, family, or a counselor about your stress.
Regular Medical Check-Ups
Frequent visits to your healthcare provider are crucial. Important aspects include:
- Routine Blood Tests: Monitor HbA1c levels, cholesterol, and kidney function.
- Eye Exams: Regular screenings for diabetic retinopathy.
- Foot Exams: Check for any sores or infections.
- Dental Check-Ups: Prevent gum disease and other dental issues.
Complications Management
Being proactive about complications can improve quality of life. Key strategies include:
- Maintain Blood Pressure and Cholesterol Levels: Follow your healthcare provider’s guidelines.
- Monitor for Symptoms: Be aware of signs of complications, such as numbness or vision changes.
- Stay Educated: Keep informed about potential complications and their prevention.
Lifestyle Changes for Long-Term Management
Adopting long-term lifestyle changes is essential. Recommendations include:
- Quit Smoking: Smoking increases the risk of diabetes complications.
- Limit Alcohol Intake: Drink in moderation, if at all.
- Stay Informed: Continually educate yourself about diabetes management.
- Build a Support Network: Surround yourself with supportive friends, family, and healthcare providers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Can diabetes be cured?
A: Currently, there is no cure for diabetes, but it can be managed effectively with lifestyle changes and medical treatments.
Q: What are the risk factors for Type 2 diabetes?
A: Risk factors include obesity, physical inactivity, family history, and age.
Q: How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
A: The frequency of monitoring depends on your treatment plan. Your healthcare provider can give you personalized advice.
Q: Is diabetes preventable?
A: Type 2 diabetes can often be prevented or delayed with a healthy lifestyle. Maintaining a balanced diet and regular exercise are key.

Hey people!!!!!
Good mood and good luck to everyone!!!!!
быстро и качественно.
Экспертные услуги сантехников в Сан-Хосе.
Быстрое устранение поломок сантехники в Сан-Хосе.
Экстренный вызов сантехника в Сан-Хосе.
Недорогие сантехнические услуги в Сан-Хосе.
Профессиональный ремонт сантехники в Сан-Хосе.
Требуется сантехник в Сан-Хосе?.
Надежные решения для вашей сантехники в Сан-Хосе.
Помощь сантехника в Сан-Хосе.
Доступные цены на сантехнические услуги в Сан-Хосе.
san jose plumbing [url=http://www.plumbersan-joseca4.com]http://www.plumbersan-joseca4.com[/url] .