

Table of Contents
Definition of Malaria:
Malaria is a life-threatening disease caused by parasites transmitted to humans through the bites of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes. It remains a major global health issue, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions.
Symptoms of Malaria:
Recognizing symptoms early is crucial for prompt treatment. Common symptoms include:
- High fever and chills
- Sweating
- Headache
- Nausea and vomiting
- Muscle pain and fatigue
- Abdominal pain and diarrhea (in some cases).

Causes of Malaria:
It is caused by Plasmodium parasites. There are five species known to infect humans:
- Plasmodium falciparum: The most deadly and widespread.
- Plasmodium vivax: Known for its dormant liver stages, causing relapses.
- Plasmodium ovale: Less common, also has dormant liver stages.
- Plasmodium malariae: Can cause chronic infection.
- Plasmodium knowlesi: Found in Southeast Asia, can be fatal.
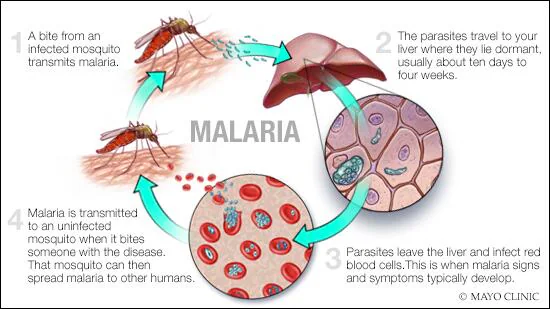
Parasites Causing Malaria:
The Plasmodium parasites responsible have complex life cycles involving two hosts: humans and mosquitoes. Once inside the human body, the parasites multiply in the liver before infecting red blood cells, leading to the symptoms.
Diagnostic Tests for Malaria:
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment. Common diagnostic methods include:
- Microscopic Examination: Blood smears are examined under a microscope to detect Plasmodium parasites.
- Rapid Diagnostic Tests (RDTs): These tests detect specific antigens in a person’s blood.
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR): Highly sensitive, used to detect and identify Plasmodium species.
- Serology Tests: Detect antibodies against malaria parasites, useful for detecting past infections.
Treatment of Malaria:
Effective treatment depends on the species of Plasmodium and the severity of the infection:
- Antimalarial Medications: Common drugs include chloroquine, artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs), and quinine.
- Supportive Care: Managing symptoms such as fever and dehydration.
- Hospitalization: Severe cases may require intensive care and intravenous medications.
Effective Management of Malaria:
Preventing and management involves a combination of strategies:
- Vector Control: Using insecticide-treated bed nets (ITNs) and indoor residual spraying (IRS) to reduce mosquito bites.
- Prophylactic Medications: For travelers to malaria-endemic areas, taking antimalarial drugs as a preventive measure.
- Vaccination: The RTS,S/AS01 (Mosquirix) vaccine provides partial protection.
- Public Health Measures: Community education, improved healthcare access, and surveillance systems to monitor and respond to outbreaks.
Conclusion:
The disease remains a significant global health challenge. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options, along with effective prevention strategies, is crucial in the fight against this disease. Stay informed and take preventive measures to protect yourself and your community.
Hey people!!!!!
Good mood and good luck to everyone!!!!!